Understanding the intricacies of taxes can feel overwhelming, but knowing how to legally reduce your tax bill before year-end can be a game changer for both individuals and businesses. As the year draws to a close, it’s crucial to explore various strategies that can lighten your financial load and maximize your returns. This overview will guide you through essential tax planning tactics that could save you money and help you navigate through common misconceptions surrounding tax responsibilities.
From taking advantage of deductions and credits to making the most of retirement contributions and charitable donations, there are several opportunities available to optimize your tax situation. With the right approach and timely actions, you can strategically position yourself for a more favorable tax outcome.
Understanding Tax Obligations
Tax obligations are a critical aspect of financial responsibility for both individuals and businesses. Understanding what these obligations entail is essential for effective financial planning and management. As the end of the year approaches, individuals and business owners alike must be aware of their tax duties and the potential strategies to minimize their liabilities. Tax obligations vary widely based on income, location, and the nature of one’s business.
Individuals typically owe taxes on earned income, while businesses must also consider taxes on profits, capital gains, and various other financial activities. Year-end tax planning becomes crucial as it allows individuals and businesses to assess their financial standing and make informed decisions to optimize their tax situations.
Importance of Year-End Tax Planning
Year-end tax planning is a proactive approach to managing tax liabilities effectively. It provides an opportunity to evaluate financial performance and make adjustments before the tax year closes. Here are several reasons why year-end tax planning is essential:
- Optimizing Deductions: Identifying available deductions can significantly lower taxable income. Common deductions include mortgage interest, charitable contributions, and business expenses.
- Contributing to Retirement Accounts: Making contributions to retirement accounts such as IRAs or 401(k)s can reduce taxable income while simultaneously saving for retirement.
- Reviewing Tax Brackets: Understanding one’s tax bracket can help in strategizing income timing, ensuring that income does not push one into a higher tax bracket unnecessarily.
- Tax Credits Utilization: Knowing which tax credits are available and applicable can lead to substantial savings. For example, credits for education or energy-efficient home improvements can provide significant benefits.
Common Misconceptions About Tax Responsibility
There are several misconceptions about tax responsibilities that can lead to misunderstandings and potentially costly mistakes. Addressing these misconceptions helps clarify tax obligations:
- Misconception: Only high-income earners owe taxes. Reality: Everyone who earns an income is responsible for paying taxes, regardless of how low that income may be.
- Misconception: Tax evasion is acceptable if one does not get caught. Reality: Tax evasion is illegal and can lead to severe penalties, including fines and imprisonment.
- Misconception: Filing taxes is unnecessary if one’s income is below a certain threshold. Reality: While lower-income earners may not owe taxes, they may still be required to file returns to claim credits or refunds.
- Misconception: Tax planning is only for businesses. Reality: Individuals can also benefit significantly from tax planning, which can lead to greater financial stability and savings.
Tax Deductions and Credits

Source: goodtimes.ca
Understanding tax deductions and credits is crucial for maximizing your tax savings before the year ends. These benefits can significantly lower your overall tax liability, allowing you to keep more of your hard-earned money. Knowing the options available to you and how to leverage them effectively can lead to substantial savings.
Common Tax Deductions Available to Taxpayers
Tax deductions reduce your taxable income, which can ultimately decrease the amount of tax you owe. Here’s a comprehensive list of common deductions that many taxpayers can utilize:
- Mortgage Interest Deduction: Homeowners can deduct the interest paid on their mortgage, up to a certain limit, which can be a significant saving.
- State and Local Taxes (SALT): Taxpayers can deduct state and local income taxes or sales taxes paid, subject to a cap of $10,000.
- Charitable Contributions: Donations made to qualified charitable organizations can be deducted, contributing to both tax savings and supporting a good cause.
- Medical Expenses: If unreimbursed medical expenses exceed 7.5% of adjusted gross income, taxpayers can deduct the excess amount.
- Student Loan Interest: Individuals can deduct interest paid on student loans, providing relief for those repaying education costs.
- Retirement Contributions: Contributions to retirement accounts like IRAs can be deducted, facilitating long-term savings while reducing taxable income.
- Business Expenses: Self-employed individuals can deduct necessary and ordinary business expenses, lowering their tax burden significantly.
Differences Between Tax Deductions and Tax Credits
Understanding the distinction between tax deductions and tax credits is vital for effective tax planning. Tax deductions lower your taxable income, while tax credits directly reduce the tax you owe, offering potentially greater savings.
Tax deductions lower your taxable income, while tax credits provide a dollar-for-dollar reduction of your tax liability.
Maximizing Deductions and Credits Before Year-End
To make the most of available deductions and credits before the year ends, consider the following strategies:
- Accelerate Expenses: Pay for deductible expenses, such as medical bills or property taxes, before December 31 to maximize your deductions for this tax year.
- Defer Income: If possible, delay receiving income until the next tax year, which can keep you in a lower tax bracket.
- Contribute to Retirement Accounts: Make contributions to retirement plans by the year-end deadline to reduce taxable income while boosting savings for the future.
- Review Charitable Contributions: Ensure that any charitable donations are made by December 31 and keep accurate records for verification.
- Utilize Tax Credits: Be aware of available credits like the Earned Income Tax Credit or Child Tax Credit, which can significantly reduce your tax bill. Make sure you qualify and claim them correctly.
Retirement Contributions
Contributing to retirement accounts before the year-end is a strategic move that can significantly lower your taxable income while securing your financial future. Making contributions to these accounts not only helps you save for retirement but also offers compelling tax benefits that can be realized in the current tax year.There are several types of retirement accounts that provide tax advantages, making it essential to understand their features and benefits.
By contributing to these accounts, you can either reduce your taxable income or allow your investments to grow tax-deferred.
Types of Retirement Accounts Offering Tax Benefits
Understanding the various retirement accounts can assist you in making informed decisions regarding your contributions. Below are some of the most common retirement accounts that provide tax benefits:
- Traditional IRA: Contributions may be tax-deductible, and growth is tax-deferred until withdrawal during retirement.
- Roth IRA: Contributions are made with after-tax dollars, but qualified withdrawals are tax-free during retirement.
- 401(k) Plans: Offered through employers, contributions can reduce your taxable income, and many employers match contributions, effectively boosting your retirement savings.
- Simplified Employee Pension (SEP) IRA: Ideal for self-employed individuals and small business owners, allowing for higher contribution limits with tax-deductible contributions.
The rules regarding contributions and deadlines vary by account type and can significantly impact the tax advantages you can claim. It’s crucial to be aware of these specifics as the year-end approaches.
Contribution Rules and Deadlines
Each retirement account has its own contribution limits and deadlines that must be adhered to in order to qualify for tax advantages. Here are key points to keep in mind:
- Traditional and Roth IRA: For 2023, the contribution limit is $6,500 ($7,500 if you’re age 50 or older). Contributions can be made until the tax filing deadline, typically April 15 of the following year.
- 401(k) Plans: For 2023, the contribution limit is $22,500 ($30,000 if you’re age 50 or older). Contributions must be made through payroll deductions before the end of the calendar year.
- SEP IRA: Contributions can be made until the tax filing deadline, including extensions, which allows for flexibility in funding your account. The contribution limit is up to 25% of compensation or $66,000 for 2023, whichever is less.
“Maximizing retirement contributions before year-end not only prepares you for the future but also offers immediate tax savings.”
Being aware of the contribution limits and deadlines is essential for making the most of your retirement savings while enjoying the tax benefits they bring. By planning your contributions strategically, you can effectively lower your tax bill and enhance your financial security for the future.
Charitable Contributions
Making charitable contributions not only helps those in need but can also provide substantial tax benefits. When you donate to qualified organizations, you can potentially reduce your taxable income, which may lower your tax bill. Understanding how these contributions work and how to document them properly is essential for maximizing your tax deductions.The IRS allows taxpayers to deduct contributions made to eligible charitable organizations, which can include cash donations, property, and even mileage driven for charitable purposes.
It’s important to note, however, that not all contributions are created equal. To qualify for a tax deduction, donations must be made to organizations recognized by the IRS as tax-exempt under section 501(c)(3).
Tax Benefits of Charitable Donations
Making charitable donations can have several tax advantages, which include:
- Reducing Taxable Income: Donations may be deducted from your taxable income, which can lower your overall tax liability.
- Potentially Lowering Tax Bracket: A significant charitable contribution might decrease your income enough to drop you into a lower tax bracket.
- Eligibility for Itemized Deductions: Donating to charity can increase your itemized deductions, often resulting in further tax savings compared to the standard deduction.
It’s essential to keep records of your donations for tax reporting. The IRS requires proper documentation to substantiate your contributions.
Documenting Charitable Contributions
Proper documentation is crucial for ensuring that your charitable contributions are deductible. Follow these steps to keep accurate records:
- Get a Receipt: Always ask for a receipt from the charity at the time of your donation. This receipt should include the charity’s name, the date of the donation, and the amount donated.
- Note Non-Cash Donations: If you donate items instead of cash, take pictures and maintain a detailed list that includes the condition of the items and their estimated fair market value.
- Record Mileage: If you drive for charitable purposes, keep a log of the miles driven, along with the purpose of each trip.
- Check Your Charity’s Status: Ensure that the organization is recognized by the IRS as a tax-exempt organization by checking the IRS’s Exempt Organizations Select Check tool.
Each of these documentation steps helps substantiate your claims should you face any questions from the IRS in the future.
Examples of Eligible Charitable Organizations
Many organizations qualify for tax-deductible contributions. Here are a few examples:
- Nonprofit Organizations: Organizations like Habitat for Humanity and the Red Cross are well-known for their charitable work.
- Educational Institutions: Donations to schools or universities, such as your local public school or scholarship funds, are typically eligible.
- Religious Organizations: Donations to churches, synagogues, mosques, and other religious institutions can also qualify.
- Health Organizations: Charities focused on health research or patient assistance, such as the American Cancer Society, are eligible for tax deductions.
Making charitable contributions can significantly benefit both the community and your financial situation. By understanding the tax implications and keeping accurate records, you can enhance your overall tax strategy while supporting causes you care about.
Business Expense Management
Managing business expenses effectively is crucial for reducing taxable income and improving overall financial health. By keeping a close eye on expenditures, businesses can ensure they are taking full advantage of available tax deductions. Maximizing deductions can lead to substantial savings, particularly as the year draws to a close and businesses prepare for tax season.The careful tracking and documentation of business expenses not only helps in preparing accurate financial statements but also supports any claims made during tax filings.
Understanding what qualifies as a business expense, and maintaining organized records, can significantly impact a business’s bottom line. Additionally, year-end adjustments to inventory can affect taxable income, making it essential to manage these factors wisely.
Common Business Expenses That Lower Taxable Income
Identifying the various expenses that are deductible can help businesses lower their taxable income. Here’s a detailed look at some common business expenses:
- Operating expenses: Costs related to running day-to-day operations, such as rent, utilities, and office supplies, are deductible.
- Employee wages and benefits: Salaries, bonuses, and employer contributions to retirement plans are all eligible for deduction.
- Depreciation: Deducting the cost of equipment and property over time helps balance taxable income with capital expenditures.
- Advertising and marketing: Funds spent on promoting a business can be deducted, aiding in both cash flow and tax reduction.
- Professional services: Fees paid to accountants, consultants, and legal advisors are deductible under business expenses.
Best Practices for Tracking and Documenting Business Expenses
Maintaining accurate records of business expenses is essential for ensuring compliance and maximizing deductions. Implementing best practices can streamline this process:
- Utilize accounting software: Programs like QuickBooks or FreshBooks allow for easy tracking and categorizing of expenses.
- Keep receipts: Store physical or digital copies of receipts for all business transactions. Consider using apps that scan and store images of receipts.
- Regularly review expenses: Conduct monthly reviews of expenditures to identify trends and opportunities for savings.
- Separate personal and business finances: Maintain separate bank accounts and credit cards for business transactions to avoid confusion during tax season.
- Consult with a tax professional: Regular check-ins with a tax advisor can provide valuable insights on deductions and compliance issues.
Tax Implications of Year-End Inventory Adjustments
Inventory valuation impacts taxable income as well. Adjusting inventory at year-end can lead to significant changes in reported income. Understanding how to calculate the cost of goods sold (COGS) and its effect on profit is necessary for tax planning.
The formula for calculating COGS is: COGS = Beginning Inventory + Purchases – Ending Inventory.
Proper inventory management allows businesses to optimize their tax strategy. If inventory levels increase, it can inflate taxable income; conversely, reducing inventory can lower taxable income. Businesses should analyze their inventory levels carefully as the year ends to ensure they’re not overpaying in taxes due to mismanagement.Effective business expense management plays a pivotal role in a company’s financial strategy. By being proactive about expenses, documenting them accurately, and understanding the implications of inventory adjustments, businesses can significantly improve their tax outcomes.
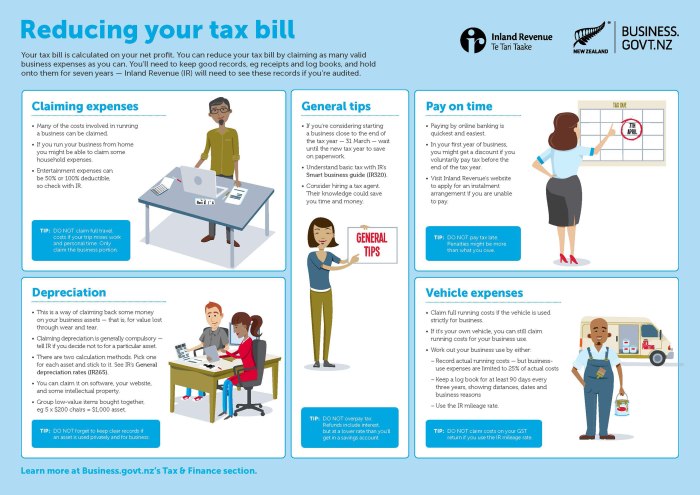
Tax-Loss Harvesting
Source: govt.nz
Tax-loss harvesting is a strategic approach that allows investors to offset capital gains by selling securities at a loss. This tactic can be particularly beneficial as year-end approaches, providing a means to lower taxable income while maintaining a balanced investment portfolio. By understanding and applying this method, individuals can take significant steps towards reducing their overall tax liability.Tax-loss harvesting involves selling underperforming investments to realize losses, which can then be used to offset gains realized from other investments.
The primary benefit of this strategy is its ability to minimize taxable income, effectively reducing the tax burden for investors. Additionally, this method can enhance portfolio performance by allowing investors to reinvest the proceeds from the sale of losses into more profitable opportunities.
Identifying Losses in Investment Portfolios
Identifying which investments to sell for tax-loss harvesting requires a thoughtful approach to analyzing your portfolio. Key steps include:
- Review your portfolio regularly to monitor performance.
- Look for securities that have depreciated in value and assess their potential for recovery.
- Consider the holding period of the asset; losses on investments held for over a year may qualify as long-term losses, which can have more favorable tax treatment.
- Utilize investment tracking tools or consult with a financial advisor to pinpoint losses effectively.
By actively managing your portfolio and keeping an eye on market trends, you can identify opportunities for tax-loss harvesting that align with your overall investment strategy.
Executing a Tax-Loss Harvesting Strategy
Successfully executing a tax-loss harvesting strategy involves a systematic approach to selling and repurchasing investments. Follow these steps to ensure you maximize your benefits:
- Sell the underperforming investments to realize the losses. Ensure that these losses exceed any gains you have for the year to maximize their tax offset potential.
- Reinvest the proceeds in similar securities to maintain your investment allocation while avoiding the wash sale rule, which disallows the deduction of losses if you buy substantially identical securities within 30 days before or after the sale.
- Document all transactions meticulously, including dates, amounts, and reasons for the sales; this will help during tax preparation.
- Consult with a tax professional to navigate the complexities of tax-loss harvesting, especially regarding specific regulations that may apply to your situation.
By implementing these steps effectively, investors can not only reduce their tax liabilities but also maintain an optimized investment strategy. The key lies in being proactive and informed throughout the process.
Timing Income and Expenses

Source: ppsfinancial.ie
Timing your income and expenses strategically can significantly impact your tax bill. By understanding how deferring income and accelerating expenses can work in your favor, you can optimize your tax position before the year ends. Making informed decisions about when to recognize income and incur expenses can lead to reduced tax liability and improved financial planning.
Deferring Income to the Following Tax Year
Deferring income to the next tax year can be a powerful strategy, especially if you anticipate being in the same or a lower tax bracket in the coming year. This allows you to delay the tax implications associated with that income. Here are a few ways to effectively defer income:
- Delay billing for services: If you run a service-based business, consider holding off on sending invoices until the new year. This keeps that income from being taxed until the following year.
- Postpone bonuses or commissions: If possible, request that bonuses or commissions be paid in January rather than December, which pushes the tax liability into the next year.
- Utilize retirement accounts: Contributing to certain retirement accounts can reduce your taxable income. If you have the option, consider deferring income by increasing your retirement contributions.
Accelerating Deductible Expenses
Accelerating deductible expenses before year-end is another effective approach. This involves incurring expenses in the current tax year to maximize your deductions. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Prepaying expenses: If you have predictable recurring expenses, consider paying them in advance. For example, pay your rent or insurance premiums for January in December.
- Stocking up on supplies: Purchase necessary supplies or inventory before the year’s end, which allows you to deduct these costs in the current tax year.
- Maximizing charitable contributions: Make charitable donations before December 31st. Not only do these contributions reduce your taxable income, but they also provide an opportunity to give back to your community.
Impact of Timing on Overall Tax Liability
The timing of your income and expenses can significantly affect your overall tax liability. By being strategic about when you recognize income and incur expenses, you can manipulate your taxable income for maximum benefit.
“Effective timing can shift your tax obligations, allowing you to manage your cash flow and retain more of your earnings.”
For instance, if you expect an increase in income or a promotion that could push you into a higher tax bracket next year, deferring income and accelerating expenses this year can be particularly advantageous. Conversely, if you foresee a drop in income, it might be better to recognize income this year and defer expenses to the next to minimize your tax burden.
Consult a Tax Professional
Engaging a tax professional can be a game-changer, especially as the year draws to a close. Their expertise can help you navigate the complex tax landscape, ensuring you capitalize on every possible deduction and credit. This proactive step not only saves you money but also reduces the stress often associated with tax season.The benefits of seeking professional tax advice are numerous.
A tax advisor can offer personalized strategies tailored to your specific financial situation, helping you to maximize your tax savings. They stay updated on the latest tax laws and regulations, which can change frequently, and they can assist in planning for future tax obligations. Furthermore, a tax professional can represent you in the event of an audit, providing peace of mind during a potentially stressful process.
Key Questions to Ask a Tax Advisor
When meeting with a tax advisor, it’s crucial to have a clear understanding of their expertise and how they can assist you effectively. Here are some key questions to consider:
- What is your experience with clients in my income bracket or industry?
- Can you explain the tax strategies you recommend for my situation?
- How do you stay updated on tax law changes?
- What is your fee structure, and are there any additional costs I should be aware of?
- How do you approach year-end tax planning?
- Can you help me with tax preparation as well as planning?
- What documentation do you need from me to get started?
- How will you communicate with me throughout the year regarding changes in my tax situation?
These inquiries can provide insight into the advisor’s qualifications, approach, and how they plan to assist you in your tax planning efforts.
Checklist for Choosing the Right Tax Professional
Selecting a suitable tax professional is crucial for maximizing your tax savings. Consider the following checklist when making your decision:
- Verify credentials and qualifications; ensure they are a certified public accountant (CPA) or an enrolled agent.
- Assess their experience with your specific financial situation or industry.
- Inquire about their fee structure and ensure it aligns with your budget.
- Request references or testimonials from previous clients.
- Ensure they have a reliable communication method and are approachable for questions throughout the year.
- Check for any disciplinary actions or complaints through state boards.
- Confirm their availability during peak tax season.
- Discuss their tax philosophy and approach to tax planning and preparation.
Using this checklist can help ensure you find a tax professional who not only meets your needs but can also provide valuable guidance as year-end approaches.
Summary
In conclusion, effectively reducing your tax bill before year-end requires a proactive and informed approach. By understanding your tax obligations, making strategic deductions, and seeking professional advice when necessary, you can significantly impact your financial standing. So, take the time to review your options and implement these strategies—your future self will thank you when tax season rolls around!
Commonly Asked Questions
What are the main tax deductions I can claim?
Common deductions include mortgage interest, student loan interest, medical expenses, and state and local taxes. Be sure to check the latest IRS guidelines for specific eligibility requirements.
Is there a limit on retirement contributions for tax benefits?
Yes, contribution limits vary by account type. For 2023, the limit for 401(k) plans is $22,500, and for IRAs, it’s $6,500. Be mindful of age-related catch-up contributions if you’re 50 or older.
How does tax-loss harvesting work?
Tax-loss harvesting involves selling underperforming investments to offset capital gains from profitable investments, thereby reducing your overall tax liability.
Can I accelerate expenses to lower my tax bill?
Yes, accelerating deductible expenses before year-end can reduce your taxable income. This can include paying bills early or purchasing necessary supplies before the year concludes.
What should I look for when choosing a tax professional?
Consider their qualifications, experience, fees, and references. It’s also important to ensure they have expertise relevant to your specific tax situation.